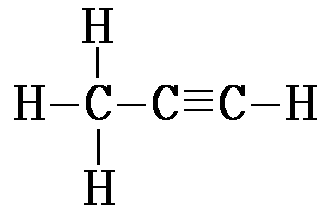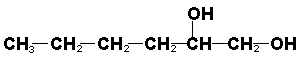| Name | General Formula | Characteristic | Example |
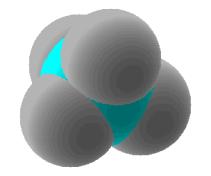
| Alkane | CnH2n+2 | single covalent bonds only |
Methane: CH4 |
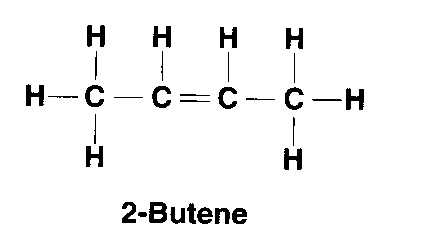
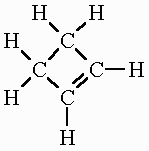
| Alkene | CnH2n | 1 double bond |
but-2-ene: C4H8 |
| Alkyne | CnH2n-2 | 1 triple bond |
prop-1-yne: C3H4 |
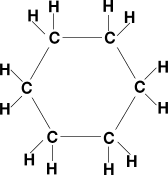
| Cycloalkane | CnH2n | ring structure, single bonds |
cyclohexane: C6H12 |
| Cycloalkene | CnH2n-2 | ring structure 1 double bonds |
cyclobutene: C4H6 |
| Alkadiene | CnH2n-2 | two double bonds |
buta-1,3-diene: C4H6 |
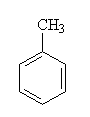
| Aromatic | CnH2n-6 | benzene ring |
toluene (1-methylbenzene). |
| Ether | R-O-R' | Oxygen single bonded in chain | 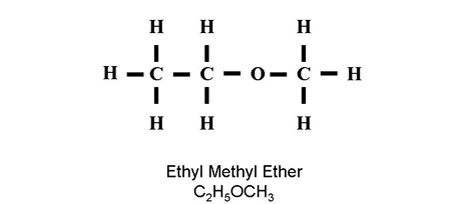
IUPAC Name: methoxyethane |
| Alcohol | R-OH | Hydroxyl in chain. |
Hexane-1,2-diol |
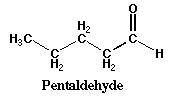
| Aldehyde | double bonded oxygen always at the end of chain |
|
|
| Ketone | double bonded oxygen in the chain |
butan-2-one |
|
| Carboxyllic acids |
O ‖RCOH |
double bonded oxygen and an OH group making a carboxyl. Always at the end. |
acetic acid (IUPAC: ethanoic acid) |
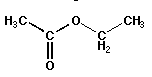
| Esters |
O ‖RCOR'
|
single bonded and double bonded oxygens separating two chains |
ethyl acetate (IUPAC: ethyl ethanoate) |
Remember we begin naming organic compounds by counting carbons in the longest continuous chain.
Prefixes
meth -- 1 Carbon
eth -- 2 Carbons
prop -- 3 Carbons
but -- 4 Carbons
pent -- 5 Carbons
hex -- 6 Carbons
hept -- 7 Carbons
oct -- 8 Carbons
non -- 9 Carbons
dec -- 10 Carbons
Great link worth the time reading: If you lose your notes go here