Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1.
What is the Universe?
a. | The next biggest part of space just past our solar system. | c. | All space and time and energy. |
b. | The idea by Stephen Hawking to explain black-holes. | d. | The part of space that we can see. |
2.
How old do scientists think the Universe is?
a. | Old Mr. K, old! | c. | 4.5 billion years |
b. | Around 20 million years. | d. | 12-15 billion years |
3.
What does red-shift mean in Astonomy?
a. | It was Edwin Hubble’s favorite football play back in college! | c. | Other galaxies must have stars that have all made it to the red giant stage of star development. |
b. | Light from galaxies that are moving away from us have the wavelengths of light stretched towards red or longer wavelengths. | d. | Light from galaxies that are moving away from us have the wavelengths of its light compressed towards blue or shorter wavelengths. |
4.
How did Edwin Hubble interpret the observation that nearly all galaxies were
red-shifted?
a. | His loaf of raisin bread had risen and was ready for the oven. | c. | All other galaxies are moving towards us then soon we can travel to other stars. |
b. | All other galaxies must have stars that “burn” a different kind of hydrogen as nuclear fuel. | d. | That all other galaxies are moving away from us, and the Universe is expanding or getting larger. |
5.
An important thick line in the absorption spectrum of stars occurs at a
wavelength of 390 nm for stars at rest (neither moving towards nor away from us). Imagine that you
observe four stars (A-D) from Earth.
Which of the stars is moving with the greatest velocity away from Earth and is furthest away?
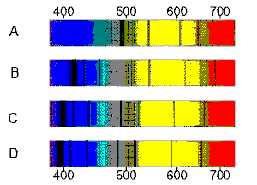
Which of the stars is moving with the greatest velocity away from Earth and is furthest away?

a. | Star A | c. | Star C |
b. | Star B | d. | Star D |
6.
n order to be a star, what must be true of a body in space?
a. | It must produce it’s own light from nuclear fusion. | c. | It must have planets orbiting it with intelligent life. |
b. | It must reflect light from a nearby sun. | d. | It must be at least 10 times more massive than our sun. |
7.
What controls how long a star will live (or be actively producing light)?
a. | How long its parents lived. | c. | Its density. Dense stars can't get as much oxygen, so the fires last longer. |
b. | Its mass, the bigger they are the faster they burn their nuclear fuel. | d. | The red-shift experienced by the 500 nm radiation. |
8.
What happens to force a star out of the main sequence?
a. | Its waves lose step with the waves of other stars | c. | It runs out of Hydrogen and starts consuming Helium |
b. | It becomes a black hole due to gravity inversion | d. | It develops planets and a solar system |
9.
Use the H-R diagram below to answer the following question.
As a star leaves its main sequence stage, it gets_____,_______,_______,_______?
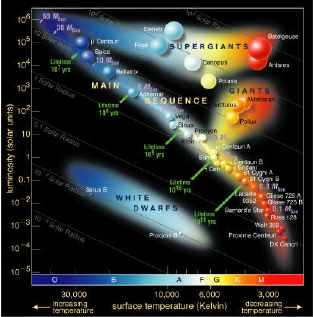
As a star leaves its main sequence stage, it gets_____,_______,_______,_______?

a. | cooler, smaller, bluer, and dimmer. | c. | cooler, larger, redder, and brighter. |
b. | hotter, larger, redder, and brighter. | d. | hotter, smaller, bluer, and dimmer. |
10.
If a star is 10 times more massive than the sun it will finally turn in to a
_________.
a. | moon | c. | black hole |
b. | giant white dwarf | d. | neutron star |