Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1.
Our neighborhood in space is called ________.
a. | Carson City | c. | the Oort Cloud |
b. | the solar system | d. | trick question Mr. K, our neighborhood. Duh! |
2.
Our sun is ___________?
a. | about 5 billion years old. | c. | the center of the solar system. |
b. | an average sized star. | d. | All of the choices are true . |
3.
Which of the following best describes the relationship between our sun and
stars.
a. | Our sun is very different from a star. It comes out during the day. Stars come out at night. | c. | Our sun is an average, mid-sized star. It is so close that we feel its it and can only see other stars at night. |
b. | Our sun is very different from a star it is yellow. Stars are white and very small. | d. | Our sun is almost a star. It concentrates and magnifies the light from thousands of stars to keep us warm like a giant magnifying glass. |
4.
Which of the following best describes the orbits of the planets?
a. | The sun is the center of the solar system and all planets orbit around it with elliptical orbits. | c. | The earth is the center of the solar system and all planets orbit around it with elliptical orbits. |
b. | The earth is the center of the solar system and all planets orbit in perfect circles around it. | d. | The sun is the center of the solar system and all the planets orbit around it in perfect circles. |
5.
Which of the following does not support the idea that the solar
system formed from a giant nebula?
a. | All planets spin the same direction (except Venus and Uranus) and the planets all orbit the same direction. | c. | Some planets are dense and small and rocky, some planets are light (low density) and very large, and gaseous. |
b. | The planets are all coplanar (except Pluto) | d. | Trick Question. All of these are true and support the idea that all planets formed from a swirling nebula. |
6.
Why are the terrestrial planets denser than the gas giants?
a. | Wrong Mr. K, the gas giants are much bigger. | c. | Volcanoes on the sun made them that way. |
b. | Iron condenses at higher temperatures than hydrogen and other gases. | d. | Hydrogen floats to the top of the solar system. It is less dense than air. |
7.
Which theory for the origin of the moon also explains the tilt of earth’s
axis by 23.5 degrees?
a. | The moon was formed from a little bit of the same material in the planetary nebula that the earth was. It might be like a drip of pancake batter falling on the griddle next to a full sized pancake. | c. | The moon was captured by the earth's gravitational field. The gravity of the moon has pulled the earth over resulting in a tilted axis. |
b. | The moon was “spun off” of the earth early on before the earth solidified. The spun off material was blob-shaped and became the moon. The earth has been wobbling ever since. | d. | The earth was hit by asteroid. The melted asteroid and parts of earth splashed into space. This debris came together to form the moon. The impact tilted earth's axis. |
8.
Which of the following correctly describes a solar eclipse.
a. | In a solar eclipse you can't see the moon, the earth passes between the moon and sun. | c. | In a solar eclipse, you can't see the moon. It passes behind the sun. |
b. | In a solar eclipse, you can't see the sun. It stops shining and reboots. | d. | In a solar eclipse, you can't see the sun, it is blocked by the moon passing in front of earth for a few minutes. |
9.
On the following diagram, which position corresponds to winter in the southern
hemisphere?
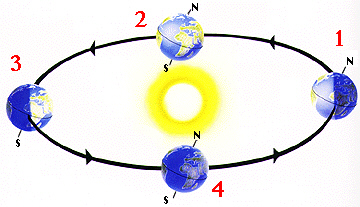

a. | Position 1 | c. | Position 3 |
b. | Position 2 | d. | Position 4 |
10.
The earth has four seasons per year because?
a. | The earth gets very near the sun and then very far away. | c. | The earth's tilt means that once a year the northern hemisphere has the sun's rays striking it at right angles. This heats up the northern hemisphere, while the southern cools. |
b. | The carbon dioxide builds up in summer time, this causes global warming in summer. | d. | The sun has 4 cycles per year, and varies between high and low output. |