4/14/2012
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers
the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
If matter is uniform throughout and cannot be separated into other substances by
physical processes, but can be decomposed into other substances by chemical processes, it is called a
(an) __________.
a. | heterogeneous mixture | b. | element | c. | homogeneous
mixture | d. | compound | e. | mixture of
elements |
|
|
|
2.
|
One side of a cube measures 1.55 m. The volume of this cube is __________
cm3.
a. | 2.40 ´ 104 | b. | 3.72 ´ 106 | c. | 2.40 | d. | 3.72 | e. | 155 |
|
|
|
3.
|
The symbol for the element lead is __________.
|
|
|
4.
|
Elements in Group 7A are known as the __________.
a. | chalcogens | b. | alkali metals | c. | alkaline earth
metals | d. | halogens | e. | noble gases |
|
|
|
5.
|
The correct name for SO is __________.
a. | sulfur oxide | b. | sulfur monoxide | c. | sulfoxide | d. | sulfate | e. | sulfite |
|
|
|
6.
|
In the periodic table, the elements are arranged in __________.
a. | alphabetical order | b. | order of increasing atomic
number | c. | order of increasing metallic properties | d. | order of increasing
neutron content | e. | reverse alphabetical order |
|
|
|
7.
|
When the following equation is balanced, the coefficient of sulfur dioxide is
__________.
PbS (s) + O2 (g) ® PbO
(s) + SO2 (g)
|
|
|
8.
|
Silver nitrate and aluminum chloride react with each other by exchanging anions:
3AgNO3 (aq)+ AlCl3 (aq) ®
Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3AgCl (s)
What mass in grams of AgCl is produced
when 4.22 g of AgNO3 react with 7.73 g of A1C13?
a. | 17.6 | b. | 4.22 | c. | 24.9 | d. | 3.56 | e. | 11.9 |
|
|
|
9.
|
Of the reactions below, which one is a decomposition reaction?
a. | NH4Cl ® NH3 +
HCl | b. | 2Mg + O2 ®
2MgO | c. | 2N2 + 3H2 ®
2NH3 | d. | 2CH4 + 4O2 ®
2CO2 + 4H2O | e. | Cd(NO3)2 +
Na2S ® CdS + 2NaNO3
|
|
|
|
10.
|
The formula weight of lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) is
__________ amu.
a. | 269.2 | b. | 285.2 | c. | 317.2 | d. | 331.2 | e. | 538.4 |
|
|
|
11.
|
How many moles of Co2+ are present in 0.200 L of a 0.400 M solution
of CoI2?
a. | 2.00 | b. | 0.500 | c. | 0.160 | d. | 0.0800 | e. | 0.0400 |
|
|
|
12.
|
The molarity of an aqueous solution containing 75.3 g of glucose
(C6H12O6) in 35.5 mL of solution is __________.
a. | 1.85 | b. | 2.12 | c. | 0.197 | d. | 3.52 | e. | 11.8 |
|
|
|
13.
|
Lead ions can be precipitated from aqueous solutions by the addition of aqueous
iodide: Pb 2+ (aq) + 2I - (aq) ®
PbI 2 (s) Lead iodide is virtually insoluble in water so that the reaction appears
to go to completion. How many milliliters of 3.550 M HI(aq) must be added to a solution containing
0.700 mol of 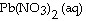 to completely precipitate the lead? a. | 2.54 ´ 10-3 | b. | 394 | c. | 197 | d. | 0.197 | e. | 0.394 |
|
|
|
14.
|
Given the following reactions
H2O (l) ® H2O (g) DH = 44.01 kJ
2H2 (g) + O2 (g) ® 2H2O
(g) DH = -483.64 kJ
the enthalpy for the decomposition of
liquid water into gaseous hydrogen and oxygen
2H2O (l) ® 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
is __________
kJ.
a. | -395.62 | b. | -527.65 | c. | 439.63 | d. | 571.66 | e. | 527.65 |
|
|
|
15.
|
Calculate the energy (J) change associated with an electron transition from n =
2 to n = 5 in a Bohr hydrogen atom. Bohr’s constant is 2.179x10-18 J
a. | 6.5 ´ 10-19 | b. | 5.5 ´ 10-19 | c. | 8.7 ´
10-20 | d. | 4.6 ´ 10-19 | e. | 5.8 ´ 10-53 |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which one of the following is the correct electron configuration for a
ground-state nitrogen atom?
a. |
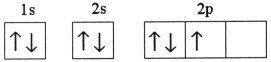 | b. |
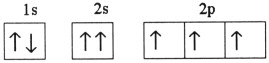 | c. |
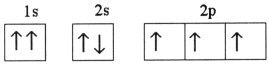 | d. |
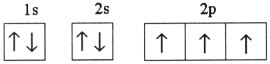 | e. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which one of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
|
|
|
18.
|
Alkali metals tend to be more reactive than alkaline earth metals because
__________.
a. | alkali metals have lower densities | b. | alkali metals have lower melting
points | c. | alkali metals have greater electron affinities | d. | alkali metals have
lower ionization energies | e. | alkali metals are not more reactive than
alkaline earth metals |
|
|
|
19.
|
Hydrogen is unique among the elements because __________.
1. It is not
really a member of any particular group.
2. Its electron is not at all shielded from its
nucleus.
3. It is the lightest element.
4. It is the only element to exist at
room temperature as a diatomic gas.
5. It exhibits some chemical properties similar to
those of groups 1A and 7A.
a. | 1, 2, 3, 5 | b. | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 | c. | 1, 4,
5 | d. | 3, 4 | e. | 2, 3, 4, 5 |
|
|
|
20.
|
Electronegativity __________ from left to right within a period and __________
from top to bottom within a group.
a. | decreases, increases | b. | increases, increases | c. | increases,
decreases | d. | stays the same, increases | e. | increases, stays the
same |
|
|
|
21.
|
A valid Lewis structure of __________ cannot be drawn without violating the
octet rule.
a. | PO43- | b. | SiF4 | c. | CF4 | d. | SeF4 | e. | NF3 |
|
|
|
22.
|
Of the possible bonds between carbon atoms (single, double, and triple),
__________.
a. | a triple bond is longer than a single bond | b. | a double bond is
stronger than a triple bond | c. | a single bond is stronger than a triple
bond | d. | a double bond is longer than a triple bond | e. | a single bond is
stronger than a double bond |
|
|
|
23.
|
The O-C-O bond angle in the CO32- ion is approximately
__________.
a. | 90° | b. | 109.5° | c. | 120° | d. | 180° | e. | 60° |
|
|
|
24.
|
According to VSEPR theory, if there are four electron domains on a central atom,
they will be arranged such that the angles between the domains are __________.
a. | 120° | b. | 109.5° | c. | 180° | d. | 360° | e. | 90° |
|
|
|
25.
|
Gaseous mixtures __________.
a. | can only contain molecules | b. | are all heterogeneous | c. | can only contain
isolated atoms | d. | are all homogeneous | e. | must contain both isolated atoms and
molecules |
|
|
|
26.
|
A fixed amount of gas at 25.0°C occupies a volume of 10.0 L when the
pressure is 629 torr. Use Charles's law to calculate the volume (L) the gas will occupy when the
temperature is increased to 121°C while maintaining the pressure at
629 torr.
a. | 10.9 | b. | 13.2 | c. | 2.07 | d. | 7.56 | e. | 48.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
27.
|
The heating curve shown was generated by measuring the heat flow and temperature
for a solid as it was heated. The slope of the __________ segment corresponds to the heat capacity of
the gas.
|
|
|
|
|
|
28.
|
Based on the figure above, the boiling point of water under an external pressure
of 0.316 atm atm is __________°C.
|
|
|
29.
|
A sealed 1.0 L flask is charged with 0.500 mol of I 2 and 0.500 mol of
Br 2. An equilibrium reaction ensues: I 2 (g) +
Br 2 (g) 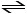 2IBr (g) When the container
contents achieve equilibrium, the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr. The value of K eq is
__________.
|
|
|
30.
|
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the weakest
base? 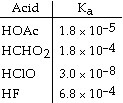 a. | OAc- | b. | CHO2- | c. | ClO- | d. | F- | e. | OAc- and
CHO2- |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which substance is the reducing agent in the following reaction?
Fe2S3 + 12HNO3 ®
2Fe(NO3)3 + 3S + 6NO2 +
6H2O
a. | HNO3 | b. | S | c. | NO2 | d. | Fe2S3 | e. | H2O |
|
|
|
32.
|
The half-life of a radionuclide
a. | is constant. | b. | gets shorter with passing
time. | c. | gets longer with passing time. | d. | gets shorter with increased
temperature. | e. | gets longer with increased temperature. |
|
|
|
33.
|
Boric oxide is __________.
a. | B2O | b. | BO2 | c. | BO | d. | B2O3 | e. | B2O4 |
|
|
|
34.
|
What happens to the silicon that is a contaminant in crude iron in a
converter?
a. | it is converted to the tetrafluoride that bubbles out as a gas. | b. | It is precipitated
as sodium silicate. | c. | It is converted to silicon dioxide and becomes
part of the slag. | d. | It is precipitated as the
carbide. | e. | It is precipitated as iron silicate. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Alkenes always contain a __________.
a. | C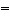 C bond C bond | b. | CºC bond | c. | C-C bond | d. | C H
bond H
bond | e. | CºH bond |
|