Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1.
Consider the following reaction:
3A ® 2B
The average rate of appearance of B is given by D[B]/Dt. Comparing the rate of appearance of B and the rate of disappearance of A, we get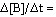
3A ® 2B
The average rate of appearance of B is given by D[B]/Dt. Comparing the rate of appearance of B and the rate of disappearance of A, we get
a. | -2/3 |
b. | +2/3 |
c. | -3/2 |
d. | +1 |
e. | +3/2 |
2.
Nitrogen dioxide decomposes to nitric oxide and oxygen via the reaction:
2NO2 ® 2NO + O2
In a particular experiment at 300°C, [NO2] drops from 0.0100 to 0.00650 M in 100 s. The rate of appearance of O2 for this period is __________ M/s.
2NO2 ® 2NO + O2
In a particular experiment at 300°C, [NO2] drops from 0.0100 to 0.00650 M in 100 s. The rate of appearance of O2 for this period is __________ M/s.
a. | 1.8 ´ 10-5 |
b. | 3.5 ´ 10-5 |
c. | 7.0 ´ 10-5 |
d. | 3.5 ´ 10-3 |
e. | 7.0 ´ 10-3 |
3.
Which substance in the reaction below either appears or disappears the fastest?
4NH3 + 7O2 ® 4NO2 + 6H2O
4NH3 + 7O2 ® 4NO2 + 6H2O
a. | NH3 |
b. | O2 |
c. | NO2 |
d. | H2O |
e. | The rates of appearance/disappearance are the same for all of these. |
A flask is charged with 0.124 mol of A and allowed to react to form
B according to the reaction A(g) ® B(g). The following data are obtained for
[A] as the reaction proceeds:

4.
The average rate of disappearance of A between 10 s and 20 s is __________
mol/s.
a. | 2.2 ´ 10-3 |
b. | 1.1 ´ 10-3 |
c. | 4.4 ´ 10-3 |
d. | 454 |
e. | 9.90 ´ 10-3 |
5.
The average rate of disappearance of A between 20 s and 40 s is __________
mol/s.
a. | 8.5 ´ 10-4 |
b. | 1.7 ´ 10-3 |
c. | 590 |
d. | 7.1 ´ 10-3 |
e. | 1.4 ´ 10-3 |
6.
How many moles of B are present at 10 s?
a. | 0.011 |
b. | 0.220 |
c. | 0.110 |
d. | 0.014 |
e. | 1.4 ´ 10-3 |
7.
If the rate law for the reaction
2A + 3B ® products
is first order in A and second order in B, then the rate law is rate = __________.
2A + 3B ® products
is first order in A and second order in B, then the rate law is rate = __________.
a. | k[A][B] |
b. | k[A]2[B]3 |
c. | k[A][B]2 |
d. | k[A]2[B] |
e. | k[A]2[B]2 |
8.
The kinetics of the reaction below were studied and it was determined that the
reaction rate increased by a factor of 9 when the concentration of B was tripled. The reaction is
__________ order in B.
A + B ® P
A + B ® P
a. | zero |
b. | first |
c. | second |
d. | third |
e. | one-half |
9.
The kinetics of the reaction below were studied and it was determined that the
reaction rate did not change when the concentration of B was tripled. The reaction is __________
order in B.
A + B ® P
A + B ® P
a. | zero |
b. | first |
c. | second |
d. | third |
e. | one-half |
10.
A reaction was found to be third order in A. Increasing the concentration of A
by a factor of 3 will cause the reaction rate to __________.
a. | remain constant |
b. | increase by a factor of 27 |
c. | increase by a factor of 9 |
d. | triple |
e. | decrease by a factor of the cube root of 3 |
The data in the table below were obtained for the reaction:
A + B ® P
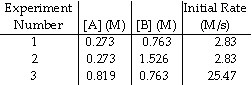
A + B ® P

11.
The order of the reaction in A is __________.
a. | 1 |
b. | 2 |
c. | 3 |
d. | 4 |
e. | 0 |
12.
The order of the reaction in B is __________.
a. | 1 |
b. | 2 |
c. | 3 |
d. | 4 |
e. | 0 |
13.
The overall order of the reaction is __________.
a. | 1 |
b. | 2 |
c. | 3 |
d. | 4 |
e. | 0 |
14.
For a first-order reaction, a plot of __________ versus __________ is
linear.
a. | ln [A]t, |
b. | ln [A]t, t |
c. | |
d. | [A]t, t |
e. | t, |
15.
The graph shown below depicts the relationship between concentration and time
for the following chemical reaction.
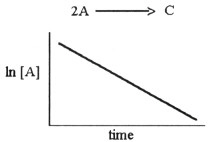
The slope of this line is equal to __________.

The slope of this line is equal to __________.
a. | k |
b. | -1/k |
c. | ln[A]o |
d. | -k |
e. | 1/k |
16.
A burning splint will burn more vigorously in pure oxygen than in air
because
a. | oxygen is a reactant in combustion and concentration of oxygen is higher in pure oxygen than is in air. |
b. | oxygen is a catalyst for combustion. |
c. | oxygen is a product of combustion. |
d. | nitrogen is a product of combustion and the system reaches equilibrium at a lower temperature. |
e. | nitrogen is a reactant in combustion and its low concentration in pure oxygen catalyzes the combustion. |
The data in the table below were obtained for the reaction:
A + B ® P
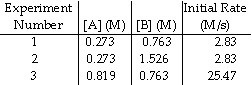
A + B ® P

17.
The rate law for this reaction is rate = __________.
a. | k[A][B] |
b. | k[P] |
c. | k[A]2[B] |
d. | k[A]2[B]2 |
e. | k[A]2 |
18.
The magnitude of the rate constant is __________.
a. | 38.0 |
b. | 0.278 |
c. | 13.2 |
d. | 42.0 |
e. | 2.21 |
19.
The reaction
CH3-NºC ® CH3-CºN
is a first-order reaction. At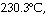
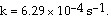 If
If 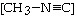 is
is 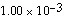 initially,
initially, 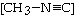 is
__________ after
is
__________ after 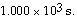
CH3-NºC ® CH3-CºN
is a first-order reaction. At
a. | 5.33 ´ 10-4 |
b. | 2.34 ´ 10-4 |
c. | 1.88 ´ 10-3 |
d. | 4.27 ´ 10-3 |
e. | 1.00 ´ 10-6 |
20.
Which one of the following graphs shows the correct relationship between
concentration and time for a reaction that is second order in [A]?
a. | 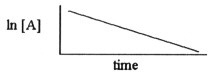 |
b. | 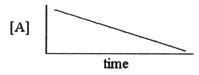 |
c. | 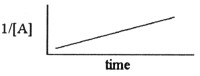 |
d. | 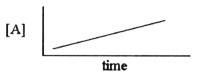 |
e. | 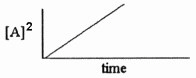 |
21.
The decomposition of N2O5 in solution in carbon
tetrachloride proceeds via the reaction
2N2O5 (soln) ® 4NO2 (soln) + O2 (soln)
The reaction is first order and has a rate constant of 4.82 ´ 10-3 s-1 at 64°C. The rate law for the reaction is rate = __________.
2N2O5 (soln) ® 4NO2 (soln) + O2 (soln)
The reaction is first order and has a rate constant of 4.82 ´ 10-3 s-1 at 64°C. The rate law for the reaction is rate = __________.
a. | k[N2O5]2 |
b. | k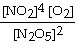 |
c. | k[N2O5] |
d. | k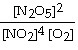 |
e. | 2k[N2O5] |
22.
Which energy difference in the energy profile below corresponds to the
activation energy for the forward reaction?
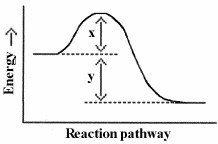

a. | x |
b. | y |
c. | x + y |
d. | x - y |
e. | y - x |
23.
In general, as temperature goes up, reaction rate __________.
a. | goes up if the reaction is exothermic |
b. | goes up if the reaction is endothermic |
c. | goes up regardless of whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic |
d. | stays the same regardless of whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic |
e. | stays the same if the reaction is first order |
24.
The mechanism for formation of the product X is:
A + B ® C + D (slow)
B + D ® X (fast)
The intermediate reactant in the reaction is __________.
A + B ® C + D (slow)
B + D ® X (fast)
The intermediate reactant in the reaction is __________.
a. | A |
b. | B |
c. | C |
d. | D |
e. | X |
25.
A catalyst can increase the rate of a reaction __________.
a. | by changing the value of the frequency factor (A) |
b. | by increasing the overall activation energy (Ea) of the reaction |
c. | by lowering the activation energy of the reverse reaction |
d. | by providing an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy |
e. | All of these are ways that a catalyst might act to increase the rate of reaction. |
26.
Nitrogen fixation is a difficult process because __________.
a. | there is so little nitrogen in the atmosphere |
b. | nitrogen exists in the atmosphere primarily as its oxides which are very unreactive |
c. | nitrogen is very unreactive, largely due to its triple bond |
d. | of the extreme toxicity of nitrogen |
e. | of the high polarity of nitrogen molecules preventing them from dissolving in biological fluids, such as those inside cells |