Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A chemical can be defined as
a. | a toxic substance. | b. | an unnatural additive placed in
food. | c. | any substance that has a definite composition. | d. | any substance that
is not alive. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The two most important properties of all matter are
a. | the ability to carry an electric current well and to hold electric
charge. | b. | taking up space and having mass. | c. | being brittle and hard. | d. | being malleable and
ductile. |
|
|
|
3.
|
An atom is
a. | the smallest unit of matter that maintains its chemical identity. | b. | the smallest unit of
a compound. | c. | always made of carbon. | d. | smaller than an
electron. |
|
|
|
4.
|
A measure of the quantity of matter is
a. | density. | c. | volume. | b. | weight. | d. | mass. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Matter includes all of the following except
a. | air. | c. | smoke. | b. | light. | d. | water vapor. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which of the following is not a physical change?
a. | grinding | c. | boiling | b. | cutting | d. | burning |
|
|
|
7.
|
Which of the following is not a chemical change?
a. | rusting | c. | melting | b. | igniting | d. | burning |
|
|
|
8.
|
A state of matter in which a material has no definite shape but has a definite
volume is the ____ state.
a. | gas | c. | plasma | b. | liquid | d. | solid |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which part of the illustration below shows the particles in a heterogeneous
mixture? 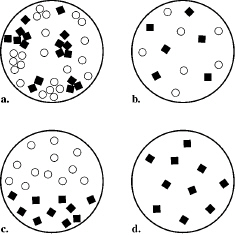
|
|
|
10.
|
The only pure substance listed below is
a. | bread dough. | c. | vitamin C (ascorbic acid). | b. | vinegar (5% acetic
acid). | d. | seawater. |
|
|
|
11.
|
A homogeneous mixture is also called
a. | chemically bonded. | c. | a solution. | b. | a compound. | d. | a solute. |
|
|
|
12.
|
All of the following are steps in the scientific method except
a. | observing and recording data. | b. | forming a hypothesis. | c. | discarding data
inconsistent with the hypothesis. | d. | developing a model based on experimental
results. |
|
|
|
13.
|
A statement that can be tested experimentally is a
a. | variable. | c. | generalization. | b. | model. | d. | hypothesis. |
|
|
|
14.
|
A theory is accepted as the explanation of an observed phenomenon until
a. | one study contradicts the theory. | b. | repeated observations conflict with the
theory. | c. | a new method is discovered. | d. | a leading scientist declares that it is
invalid. |
|
|
|
15.
|
All of the following are examples of units except
a. | mass. | c. | gram. | b. | kilometer. | d. | ounce. |
|
|
|
16.
|
Which of these is not an SI base unit?
a. | kilogram | c. | liter | b. | second | d. | Kelvin |
|
|
|
17.
|
The symbol mm represents
a. | micrometer. | c. | milliliter. | b. | millimeter. | d. | meter. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of these symbols represents a unit of volume?
|
|
|
19.
|
The relationship between the mass m of a material, its volume V,
and its density D is
a. | D = mV. | c. | D = m/V. | b. | D = V/m. | d. | D = m +
v. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which of these statements about density is true?
a. | Larger objects are more dense. | b. | Density does not depend on
temperature. | c. | Density is a physical property. | d. | The density of an object depends on the force
of gravity. |
|
|
|
21.
|
The density of aluminum is 2.70 g/cm3. What is the mass of a solid
piece of aluminum with a volume of 1.50 cm3?
a. | 0.556 g | c. | 4.05 g | b. | 1.80 g | d. | 4.20 g |
|
|
|
22.
|
100 milliliters is equivalent to
a. | 1 hectoliter. | c. | 1 centiliter. | b. | 1 microliter. | d. | 1 deciliter. |
|
|
|
23.
|
The number of grams equal to 0.5 kg is
a. | 0.0005. | c. | 500. | b. | 0.005. | d. | 5000. |
|
|
|
24.
|
How many minutes are in 1 week?
a. | 168 min | c. | 10 080 min | b. | 1440 min | d. | 100 800 min |
|
|
|
25.
|
If 1 inch equals 2.54 cm, how many centimeters equal 1 yard?
a. | 0.0706 cm | c. | 30.5 cm | b. | 14.2 cm | d. | 91.4 cm |
|
|
|
26.
|
The measurement 0.035550 g rounded off to two significant figures would
be
a. | 0.03 g. | c. | 0.036 g. | b. | 0.35 g. | d. | 3.5 ´
102 g. |
|
|
|
27.
|
When adding numbers, the sum should be rounded so that the final digit is in the
same place as the
a. | rightmost digit of the numbers added. | b. | last digit in the longest number
added. | c. | leftmost digit of the numbers added. | d. | leftmost digit of the shortest number
added. |
|
|
|
28.
|
How is the measurement 0.000 065 cm written in scientific notation?
a. | 65 ´ 10–6 cm | c. | 6.5 ´ 10–6 cm | b. | 6.5 ´
10–5 cm | d. | 6.5 ´ 10–4
cm |
|
|
|
29.
|
The measurement 0.020 L is the same as
a. | 2.0 ´ 10–3 L. | c. | 2.0 ´ 10–2 L. | b. | 2.0 ´
102 L. | d. | 2.0 ´ 10–1 L. |
|
|
|
30.
|
If each atom of element D has 3 mass units and each atom of element E has 5 mass
units, a molecule composed of one atom each of D and E has
a. | 2 mass units. | c. | 15 mass units. | b. | 8 mass units. | d. | 35 mass units. |
|
|
|
31.
|
According to the law of definite proportions, any two samples of KCl have
a. | the same mass. | c. | the same melting point. | b. | slightly different
molecular structures. | d. | the
same ratio of elements. |
|
|
|
32.
|
According to the law of conservation of mass, when sodium, hydrogen, and oxygen
react to form a compound, the mass of the compound is ____ the sum of the masses of the individual
elements.
a. | equal to | c. | less than | b. | greater than | d. | either greater than or less
than |
|
|
|
33.
|
Experiments with cathode rays led to the discovery of the
a. | proton. | c. | neutron. | b. | nucleus. | d. | electron. |
|
|
|
34.
|
In Rutherford's experiments, alpha particles
a. | passed through a tube containing gas. | c. | collided with
electrons. | b. | were used to bombard a cathode plate. | d. | were used to bombard thin metal
foil. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Because most particles fired at metal foil passed straight through, Rutherford
concluded that
a. | atoms were mostly empty space. | c. | electrons formed the
nucleus. | b. | atoms contained no charged particles. | d. | atoms were
indivisible. |
|
|
|
36.
|
A nuclear particle that has about the same mass as a proton, but with no
electrical charge, is called a(n)
a. | nuclide. | c. | electron. | b. | neutron. | d. | isotope. |
|
|
|
37.
|
The nucleus of an atom has all of the following characteristics except
that it
a. | is positively charged. | b. | is very dense. | c. | contains nearly all
of the atom's mass. | d. | contains nearly all of the atom's
volume. |
|
|
|
38.
|
The smallest unit of an element that can exist either alone or in combination
with other such particles of the same or different elements is the
a. | electron. | c. | neutron. | b. | proton. | d. | atom. |
|
|
|
39.
|
All isotopes of hydrogen contain
a. | one neutron. | c. | one proton. | b. | two electrons. | d. | two nuclei. |
|
|
|
40.
|
As the mass number of an element’s isotopes of an element increases, the
number of protons
a. | decreases. | b. | increases. | c. | remains the
same. | d. | doubles each time the mass number increases. |
|
|
|
41.
|
An aluminum isotope consists of 13 protons, 13 electrons, and 14 neutrons. Its
mass number is
|
|
|
42.
|
Because excited hydrogen atoms always produce the same line-emission spectrum,
scientists concluded that hydrogen
a. | had no electrons. | b. | did not release photons. | c. | released photons of
only certain energies. | d. | could only exist in the ground
state. |
|
|
|
43.
|
For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited
state,
a. | energy must be released. | b. | energy must be absorbed. | c. | radiation must be
emitted. | d. | the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy
level. |
|
|
|
44.
|
Bohr's theory helped explain why
a. | electrons have negative charge. | b. | most of the mass of the atom is in the
nucleus. | c. | excited hydrogen gas gives off certain colors of light. | d. | atoms combine to
form molecules. |
|
|
|
45.
|
The set of orbitals that are dumbbell shaped and directed along the x,
y, and z axes are called
a. | d orbitals. | c. | f orbitals. | b. | p orbitals. | d. | s
orbitals. |
|
|
|
46.
|
A spherical electron cloud surrounding an atomic nucleus would best
represent
a. | an s orbital. | b. | a px
orbital. | c. | a combination of px and py
orbitals. | d. | a combination of an s and a px
orbital. |
|
|
|
47.
|
The major difference between a 1s orbital and a 2s orbital is
that
a. | the 2s orbital can hold more electrons. | b. | the 2s
orbital has a slightly different shape. | c. | the 2s orbital is at a higher energy
level. | d. | the 1s orbital can have only one electron. |
|
|
|
48.
|
The p orbitals are shaped like
a. | electrons. | c. | dumbbells. | b. | circles. | d. | spheres. |
|
|
|
49.
|
The number of orbitals for the d sublevel is
|
|
|
50.
|
Which of the following lists atomic orbitals in the correct order they are
filled according to the Aufbau principle?
a. | 1s 2s 2p 3s 4s 3p 3d 4p
5s | b. | 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p
5s | c. | 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 4p 3d
4d | d. | 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p
5s |
|
|
|
51.
|
The element with electron configuration 1s2
2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 is
a. | Mg (Z = 12). | c. | S (Z = 16). | b. | C (Z = 6). | d. | Si (Z =
14). |
|
|
|
52.
|
The electron configuration for the carbon atom (C) is 1s2
2s2 2p2. The atomic number of carbon is
|
|
|
53.
|
What is the electron configuration for nitrogen, atomic number 7?
a. | 1s2 2s2 2p3 | b. | 1s2 2s3 2p2 | c. | 1s2 2s3 2p1 | d. | 1s2 2s2 2p2
3s1 |
|
|
|
54.
|
Argon, krypton, and xenon are
a. | alkaline earth metals. | c. | actinides. | b. | noble gases. | d. | lanthanides. |
|
|
|
55.
|
Elements in a group or column in the periodic table can be expected to have
similar
a. | atomic masses. | c. | numbers of neutrons. | b. | atomic numbers. | d. | properties. |
|
|
|
56.
|
Elements to the right side of the periodic table (p-block elements) have
properties most associated with
a. | gases. | c. | metals. | b. | nonmetals. | d. | metalloids. |
|
|
|
57.
|
Elements in which the d-sublevel is being filled have the properties
of
a. | metals. | c. | metalloids. | b. | nonmetals. | d. | gases. |
|
|
|
58.
|
The group of soft, silvery, reactive metals, all of which have one electron in
an s orbital, is known as the
a. | alkaline-earth metals. | c. | alkali metals. | b. | transition metals. | d. | metalloids. |
|
|
|
59.
|
Compared to the alkali metals, the alkaline-earth metals
a. | are less reactive. | b. | have lower melting points. | c. | are less
dense. | d. | combine more readily with nonmetals. |
|
|
|
60.
|
When an electron is added to a neutral atom, a certain amount of energy
is
a. | always absorbed. | b. | always released. | c. | either released or
absorbed. | d. | transferred to the more electronegative element. |
|
|
|
61.
|
Which represents a neutral atom acquiring an electron in a process where energy
is released?
a. | A + e– + energy ®
A– | b. | A + e– ® A– – energy | c. | A +
e– ® A– +
energy | d. | A– + energy ® A +
e– |
|
|
|
62.
|
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is the atom's
a. | electron affinity. | c. | electronegativity. | b. | electron energy. | d. | ionization
energy. |
|
|
|
63.
|
A measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
from another atom in the compound is called
a. | electron affinity. | c. | electronegativity. | b. | electron configuration. | d. | ionization
potential. |
|
|
|
64.
|
The element that has the greatest electronegativity is
a. | oxygen. | c. | chlorine. | b. | sodium. | d. | fluorine. |
|
|
|
65.
|
A positive ion is known as a(n)
a. | ionic radius. | c. | cation. | b. | valence electron. | d. | anion |
|
|
|
66.
|
Across a period in the periodic table, atomic radii
a. | gradually decrease. | b. | gradually decrease, then sharply
increase. | c. | gradually increase. | d. | gradually increase, then sharply
decrease. |
|
|
|
67.
|
A mutual electrical attraction between the nuclei and valence electrons of
different atoms that binds the atoms together is called a(n)
a. | dipole. | c. | chemical bond. | b. | Lewis structure. | d. | London force. |
|
|
|
68.
|
Malleability and ductility are characteristic of substances with
a. | covalent bonds. | c. | Lewis structures. | b. | ionic bonds. | d. | metallic bonds. |
|
|
|
69.
|
A chemical formula includes the symbols of the elements in the compound and
subscripts that indicate
a. | atomic mass of each element. | b. | number of atoms or ions of each element that
are combined in the compound. | c. | formula mass. | d. | charges on the
elements or ions. |
|
|
|
70.
|
How many atoms of fluorine are present in a molecule of carbon tetrafluoride,
CF4?
|
|
|
71.
|
What is the formula for zinc fluoride?
|
|
|
72.
|
What is the formula for the compound formed by calcium ions and chloride
ions?
a. | CaCl | c. | CaCl3 | b. | Ca2Cl | d. | CaCl2 |
|
|
|
73.
|
What is the formula for the compound formed by lead(II) ions and chromate
ions?
a. | PbCrO4 | c. | Pb2(CrO4)3 | b. | Pb2CrO4 | d. | Pb(CrO4)2 |
|
|
|
74.
|
What is the formula for aluminum sulfate?
a. | AlSO4 | c. | Al2(SO4)3 | b. | Al2SO4 | d. | Al(SO4)3 |
|
|
|
75.
|
What is the formula for barium hydroxide?
a. | BaOH | c. | Ba(OH)2 | b. | BaOH2 | d. | Ba(OH) |
|
|
|
76.
|
Name the compound Ni(ClO3)2.
a. | nickel(II) chlorate | c. | nickel(II) chlorite | b. | nickel(II) chloride | d. | nickel(II)
peroxide |
|
|
|
77.
|
Name the compound Zn3(PO4)2.
a. | zinc potassium oxide | c. | zinc phosphate | b. | trizinc polyoxide | d. | zinc phosphite |
|
|
|
78.
|
Name the compound KClO3.
a. | potassium chloride | c. | potassium chlorate | b. | potassium trioxychlorite | d. | hypochlorite |
|
|
|
79.
|
Name the compound Fe(NO3)2.
a. | iron(II) nitrate | c. | iron(III) nitrate | b. | iron(II) nitrite | d. | iron(III)
nitride |
|