Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Electromagnetic radiation travels through vacuum at a speed of __________
m/s.
a. | 186,000 | b. | 125 | c. | 3.00 ´ 108 | d. | 10,000 | e. | It depends on
wavelength. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The wavelength of light that has a frequency of 1.20 ´ 1013 s-1 is __________ m.
a. | 25.0 | b. | 2.50 ´
10-5 | c. | 0.0400 | d. | 12.0 | e. | 2.5 |
|
|
|
3.
|
The energy of a photon of light is __________ proportional to its frequency and
__________ proportional to its wavelength.
a. | directly, directly | b. | inversely, inversely | c. | inversely,
directly | d. | directly, inversely | e. | indirectly, not |
|
|
|
4.
|
Of the following, __________ radiation has the shortest wavelength.
a. | X-ray | b. | radio | c. | microwave | d. | ultraviolet | e. | infrared |
|
|
|
5.
|
A mole of red photons of wavelength 725 nm has __________ kJ of energy.
a. | 2.74 ´ 10-19 | b. | 4.56 ´ 10-46 | c. | 6.05 ´
10-3 | d. | 165 | e. | 227 |
|
|
|
6.
|
It takes 254 kJ/mol to eject electrons from a certain metal surface. What is the
longest wavelength of light (nm) that can be used to eject electrons from the surface of this metal
via the photoelectric effect?
a. | 471 | b. | 233 | c. | 165 | d. | 725 | e. | 552 |
|
|
|
7.
|
Of the following transitions in the Bohr hydrogen atom, the __________
transition results in the emission of the highest-energy photon.
a. | n = 1 ® n = 6 | b. | n = 6 ® n = 1 | c. | n = 6 ® n =
3 | d. | n = 3 ® n = 6 | e. | n = 1 ® n = 4 |
|
|
|
8.
|
When the electron in a hydrogen atom moves from n = 6 to n = 2, light with a
wavelength of __________ nm is emitted.
a. | 93.8 | b. | 434 | c. | 487 | d. | 657 | e. | 410 |
|
|
|
9.
|
The __________ quantum number defines the shape of an orbital.
a. | spin | b. | magnetic | c. | principal | d. | azimuthal | e. | psi |
|
|
|
10.
|
The __________ subshell contains only one orbital.
|
|
|
11.
|
The azimuthal quantum number is 3 in __________ orbitals.
|
|
|
12.
|
__________-orbitals are spherically symmetrical.
|
|
|
13.
|
Each p-subshell can accommodate a maximum of __________ electrons.
|
|
|
14.
|
The 4d subshell in the ground state of atomic xenon contains __________
electrons.
|
|
|
15.
|
There are __________ unpaired electrons in a ground state phosphorus
atom.
|
|
|
16.
|
The ground state electron configuration for Zn is __________.
a. | [Kr]4s23d10 | b. | [Ar]4s23d10 | c. | [Ar]4s13d10 | d. | [Ar]3s23d10 | e. | [Kr]3s23d10 |
|
|
|
17.
|
All of the __________ have a valence shell electron configuration
ns1.
a. | noble gases | b. | halogens | c. | chalcogens | d. | alkali metals | e. | alkaline earth
metals |
|
|
|
18.
|
The photoelectric effect is __________.
a. | the total reflection of light by metals giving them their typical
luster | b. | the production of current by silicon solar cells when exposed to
sunlight | c. | the ejection of electrons by a metal when struck with light of sufficient
energy | d. | the darkening of photographic film when exposed to an electric
field | e. | a relativistic effect |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which one of the following is the correct electron configuration for a
ground-state nitrogen atom?
a. |
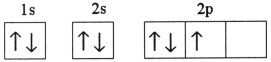 | b. |
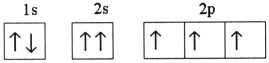 | c. |
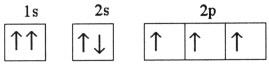 | d. |
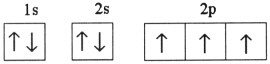 | e. | None of the above is correct. |
|
|
|
20.
|
The ground state electron configuration of Fe is __________.
a. | 1s22s23s23p63d6 | b. | 1s22s22p63s23p63d64s2 | c. | 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 | d. | 1s22s22p63s23p64s24d6 | e. | 1s22s23s23p10 |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which two elements have the same ground-state electron configuration?
a. | Pd and Pt | b. | Cu and Ag | c. | Fe and
Cu | d. | Cl and Ar | e. | No two elements have the same ground-state
electron configuration. |
|