Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
There are __________ paired and __________ unpaired electrons in the Lewis
symbol for a phosphorus atom.
a. | 4, 2 | b. | 2, 4 | c. | 2,
3 | d. | 4, 3 | e. | 0, 3 |
|
|
|
2.
|
Based on the octet rule, magnesium most likely forms a __________ ion.
a. | Mg2+ | b. | Mg2- | c. | Mg6- | d. | Mg6+ | e. | Mg- |
|
|
|
3.
|
How many unpaired electrons are there in the Lewis structures of a
N3- ion?
a. | 0 | b. | 1 | c. | 2 | d. | 3 | e. | This cannot be
predicted. |
|
|
|
4.
|
For a given arrangement of ions, the lattice energy increases as ionic radius
__________ and as ionic charge __________.
a. | decreases, increases | b. | increases, decreases | c. | increases,
increases | d. | decreases, decreases | e. | This cannot be
predicted. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Elements from opposite sides of the periodic table tend to form
__________.
a. | covalent compounds | b. | ionic compounds | c. | compounds that are
gaseous at room temperature | d. | homonuclear diatomic
compounds | e. | covalent compounds that are gaseous at room
temperature |
|
|
|
6.
|
Determining lattice energy from Born-Haber cycle data requires the use of
__________.
a. | the octet rule | b. | Coulomb's law | c. | Periodic
law | d. | Hess's law | e. | Avogadro's
number |
|
|
|
7.
|
A double bond consists of __________ pairs of electrons shared between two
atoms.
|
|
|
8.
|
What is the maximum number of double bonds that a hydrogen atom can form?
|
|
|
9.
|
In the molecule below, which atom has the largest partial negative charge
__________? 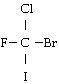
|
|
|
10.
|
The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons is best quantified by
the __________.
a. | paramagnetism | b. | diamagnetism | c. | electronegativity | d. | electron change-to-mass
ratio | e. | first ionization potential |
|
|
|
11.
|
Given the electronegativities below, which covalent single bond is most
polar? | Element: | H | C | N | O | | Electronegativity: | 2.1 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | | | | | |
a. | C-H | b. | N-H | c. | O-H | d. | O-C | e. | O-N |
|
|
|
12.
|
Electronegativity __________ from left to right within a period and __________
from top to bottom within a group.
a. | decreases, increases | b. | increases, increases | c. | increases,
decreases | d. | stays the same, increases | e. | increases, stays the
same |
|
|
|
13.
|
A nonpolar bond will form between two __________ atoms of __________
electronegativity.
a. | different, opposite | b. | identical, different | c. | different,
different | d. | similar, different | e. | identical,
equal |
|
|
|
14.
|
The formal charge on carbon in the molecule below is __________. 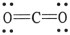
|
|
|
15.
|
The formal charge on nitrogen in NO 3- is __________.
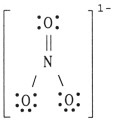
|
|
|
16.
|
Using the table of average bond energies below, the DH for the reaction is __________ kJ. 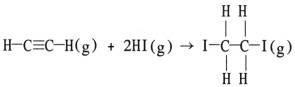 | Bond: | CºC | C=C | H-I | C-I | C-H | | D
(kJ/mol): | 839 | 348 | 299 | 240 | 413 | | | | | | |
a. | +160 | b. | -160 | c. | -217 | d. | -63 | e. | +63 |
|
|
|
17.
|
Using the table of average bond energies below, the DH for the reaction is __________ kJ. H – C ºC–H (g) + H–I (g) ® H 2C=CHI (g) | Bond: | CºC | C=C | H-I | C-I | C-H | | D
(kJ/mol): | 839 | 614 | 299 | 240 | 413 | | | | | | |
a. | +506 | b. | -931 | c. | -506 | d. | -129 | e. | +129 |
|
|
|
18.
|
Lattice energy is __________.
a. | the energy required to convert a mole of ionic solid into its constituent ions in the
gas phase | b. | the energy given off when gaseous ions combine to form one mole of an ionic
solid | c. | the energy required to produce one mole of an ionic compound from its constituent
elements in their standard states | d. | the sum of ionization energies of the
components in an ionic solid | e. | the sum of electron affinities of the
components in an ionic solid |
|
|
|
19.
|
The diagram below is the Born-Huber cycle for the formation of crystalline
potassium fluoride. 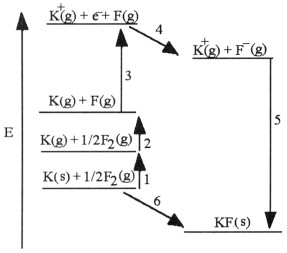 Which energy change corresponds to the
electron affinity of fluorine?
|
|
|
20.
|
The diagram below is the Born-Huber cycle for the formation of crystalline
potassium fluoride. 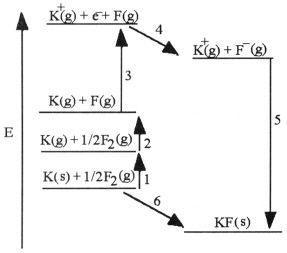 Which energy change corresponds to the
first ionization energy of potassium?
|
|
|
21.
|
In which of the molecules below is the carbon-carbon distance the
shortest?
a. | H2C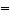 CH2 CH2 | b. | H-CºC-H | c. | H3C-CH3 | d. | H2C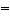 C C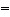 CH2 CH2 | e. | H3C-CH2-CH3 |
|
|
|
22.
|
The Lewis structure of the CO32- ion is __________.
|
|
|
23.
|
Resonance structures differ by __________.
a. | number and placement of electrons | b. | number of electrons only | c. | placement of atoms
only | d. | number of atoms only | e. | placement of electrons
only |
|
|
|
24.
|
For resonance forms of a molecule or ion, __________.
a. | one always corresponds to the observed structure | b. | all the resonance
structures are observed in various proportions | c. | the observed structure is an average of the
resonance forms | d. | the same atoms need not be bonded to each other in all resonance
forms | e. | there cannot be more than two resonance structures for a given
species |
|
|
|
25.
|
The central atom in __________ violates the octet rule.
a. | NH3 | b. | SeF2 | c. | BF3 | d. | AsF3 | e. | CF4 |
|
|
|
26.
|
A valid Lewis structure of __________ cannot be drawn without violating the
octet rule.
a. | ClF3 | b. | PCl3 | c. | SO3 | d. | CCl4 | e. | CO2 |
|
|
|
27.
|
Which atom can accommodate an octet of electrons, but doesn't necessarily
have to accommodate an octet?
|
|
|
28.
|
Of the bonds C-N, C 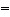 N, and C ºN,
the C-N bond is __________. a. | strongest/shortest | b. | strongest/longest | c. | weakest/shortest | d. | weakest/longest | e. | intermediate in both
strength and length |
|