Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A pressure of 1.00 atm is the same as a pressure of __________ of mm Hg.
a. | 193 | b. | 101 | c. | 760. | d. | 29.9 | e. | 33.0 |
|
|
|
2.
|
A gas vessel is attached to an open-end manometer containing a nonvolatile
liquid of density 0.791 g/mL as shown below. 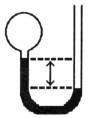 The
difference in heights of the liquid in the two sides of the manometer is 43.4 cm when the atmospheric
pressure is 755 mm Hg. Given that the density of mercury is 13.6 g/mL, the pressure of the
enclosed gas is __________ atm. a. | 1.03 | b. | 0.960 | c. | 0.993 | d. | 0.990 | e. | 0.987 |
|
|
|
3.
|
A sample of gas (24.2 g) initially at 4.00 atm was compressed from 8.00 L to
2.00 L at constant temperature. After the compression, the gas pressure was __________
atm.
a. | 4.00 | b. | 2.00 | c. | 1.00 | d. | 8.00 | e. | 16.0 |
|
|
|
4.
|
A balloon originally had a volume of 4.39 L at 44 °C and a pressure of 729
torr. The balloon must be cooled to __________°C to reduce its volume to 3.78 L (at
constant pressure).
|
|
|
5.
|
If 50.75 g of a gas occupies 10.0 L at STP, 129.3 g of the gas will occupy
__________ L at STP.
a. | 3.92 | b. | 50.8 | c. | 12.9 | d. | 25.5 | e. | 5.08 |
|
|
|
6.
|
A sample of an ideal gas (3.00 L) in a closed container at 25.0°C and 76.0
torr is heated to 300 °C. The pressure of the gas at this temperature is __________
torr.
a. | 912 | b. | 146 | c. | 76.5 | d. | 39.5 | e. | 2.53 ´ 10-2 |
|
|
|
7.
|
The amount of gas that occupies 60.82 L at 31°C and 367 mm Hg is __________
mol.
a. | 1.18 | b. | 0.850 | c. | 894 | d. | 11.6 | e. | 0.120 |
|
|
|
8.
|
The molecular weight of a gas is __________ g/mol if 3.5 g of the gas occupies
2.1 L at STP.
a. | 41 | b. | 5.5 ´
103 | c. | 37 | d. | 4.6 ´
102 | e. | 2.7 ´ 10-2 |
|
|
|
9.
|
The molecular weight of a gas that has a density of 5.75 g/L at STP is
__________ g/mol.
a. | 3.90 | b. | 129 | c. | 141 | d. | 578 | e. | 1.73 ´ 10-3 |
|
|
|
10.
|
Automobile air bags use the decomposition of sodium azide as their source of gas
for rapid inflation:
2NaN3 (s) ® 2Na
(s) + 3N2 (g).
What mass (g) of NaN3 is required to provide
40.0 L of N2 at 25.0°C and 763 torr?
a. | 1.64 | b. | 1.09 | c. | 160 | d. | 71.1 | e. | 107 |
|
|
|
11.
|
Since air is a mixture, it does not have a "molar mass."
However, for calculation purposes, it is possible to speak of its "effective molar
mass." (An effective molar mass is a weighted average of the molar masses of a
mixture's components.) If air at STP has a density of 1.285 g/L, its effective molar mass
is __________ g/mol.
a. | 26.94 | b. | 31.49 | c. | 30.00 | d. | 34.42 | e. | 28.80 |
|
|
|
12.
|
In a gas mixture of He, Ne, and Ar with a total pressure of 8.40 atm, the mole
fraction of Ar is __________ if the partial pressures of He and Ne are 1.50 and 2.00 atm,
respectively.
a. | 0.179 | b. | 0.238 | c. | 0.357 | d. | 0.583 | e. | 0.417 |
|
|
|
13.
|
A gas mixture of Ne and Ar has a total pressure of 4.00 atm and contains 16.0
mol of gas. If the partial pressure of Ne is 2.75 atm, how many moles of Ar are in the
mixture?
a. | 11.0 | b. | 5.00 | c. | 6.75 | d. | 9.25 | e. | 12.0 |
|
|
|
14.
|
A mixture of He and Ne at a total pressure of 0.95 atm is found to contain 0.32
mol of He and 0.56 mol of Ne. The partial pressure of Ne is __________ atm.
a. | 1.7 | b. | 1.5 | c. | 0.60 | d. | 0.35 | e. | 1.0 |
|
|
|
15.
|
SO2 (5.00 g) and CO2 (5.00 g) are placed in a 750.0 mL
container at 50.0°C. The partial pressure of SO2 in the container was
__________ atm.
a. | 2.76 | b. | 4.02 | c. | 6.78 | d. | 0.192 | e. | 1.60 |
|
|
|
16.
|
A sample of He gas (2.0 mmol) effused through a pinhole in 53 s. The
same amount of an unknown gas, under the same conditions, effused through the pinhole in 248 s.
The molecular mass of the unknown gas is __________ g/mol.
|
|
|
17.
|
Which of the following statements about gases is false?
a. | Gases are highly compressible. | b. | Distances between molecules of gas are very
large compared to bond distances within molecules. | c. | Non-reacting gas mixtures are
homogeneous. | d. | Gases expand spontaneously to fill the container they are placed
in. | e. | All gases are colorless and odorless at room
temperature. |
|
|
|
18.
|
The volume of an ideal gas is zero at __________.
a. | 0°C | b. | -45°F | c. | -273
K | d. | -363 K | e. | -273°C |
|