Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The first law of thermodynamics can be given as __________.
a. | DE = q + w | b. | 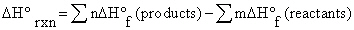 | c. | for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the
universe increases | d. | the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at
absolute zero is zero | e. | DS =
qrev/T at constant temperature |
|
|
|
2.
|
A reaction that is spontaneous as written __________.
a. | is very rapid | b. | will proceed without outside
intervention | c. | is also spontaneous in the reverse direction | d. | has an equilibrium
position that lies far to the left | e. | is very slow |
|
|
|
3.
|
When a system is at equilibrium, __________.
a. | the reverse process is spontaneous but the forward process is not | b. | the forward and the
reverse processes are both spontaneous | c. | the forward process is spontaneous but the
reverse process is not | d. | the process is not spontaneous in either
direction | e. | both forward and reverse processes have stopped |
|
|
|
4.
|
The thermodynamic quantity that expresses the degree of disorder in a system is
__________.
a. | enthalpy | b. | internal energy | c. | bond
energy | d. | entropy | e. | heat flow |
|
|
|
5.
|
Which one of the following is always positive when a spontaneous process
occurs?
a. | DSsystem | b. | DSsurroundings | c. | DSuniverse | d. | DHuniverse | e. | DHsurroundings |
|
|
|
6.
|
The second law of thermodynamics states that __________.
a. | DE = q + w | b. | DH°rxn = S nDH°f (products) - S mDH°f (reactants) | c. | for any spontaneous process, the entropy of the
universe increases | d. | the entropy of a pure crystalline substance is
zero at absolute zero | e. | DS =
qrev/T at constant temperature |
|
|
|
7.
|
The normal boiling point of water is 100.0°C and its molar enthalpy of
vaporization is 40.67 kJ/mol. What is the change in entropy in the system in J/K when 39.3 grams of
steam at 1 atm condenses to a liquid at the normal boiling point?
a. | 88.8 | b. | -88.8 | c. | -238 | d. | 373 | e. | -40.7 |
|
|
|
8.
|
DS is positive for the reaction __________.
a. | 2H2 (g) + O2 (g) ®
2H2O (g) | b. | 2NO2 (g) ® N2O4 (g) | c. | CO2 (g)
® CO2 (s) | d. | BaF2 (s) ® Ba2+ (aq) + 2F-
(aq) | e. | 2Hg (l) + O2 (g) ® 2HgO
(s) |
|
|
|
9.
|
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of __________ is zero.
(a) H2O (l)
(b) Na (s)
(c) H2 (g)
a. | (a) only | b. | (b) only | c. | (c)
only | d. | (b) and (c) | e. | (a), (b), and
(c) |
|
|
|
10.
|
For the reaction
C2H6 (g) ® C2H4 (g) + H2
(g)
DH° is +137 kJ/mol and DS°
is +120 J/K • mol. This reaction is __________.
a. | spontaneous at all temperatures | b. | spontaneous only at high
temperature | c. | spontaneous only at low temperature | d. | nonspontaneous at all
temperatures |
|
|
|
11.
|
A reaction that is not spontaneous at low temperature can become spontaneous at
high temperature if DH is __________ and DS is
__________.
a. | +, + | b. | -, - | c. | +,
- | d. | -, + | e. | +, 0 |
|
|
|
12.
|
If DG° for a reaction is greater than zero, then
__________.
a. | K = 0 | b. | K = 1 | c. | K >
1 | d. | K < 1 | e. | More information is
needed. |
|