Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1.
What is the conjugate acid of NH3?
a. | NH3 |
b. | NH2+ |
c. | NH3+ |
d. | NH4+ |
e. | NH4OH |
2.
The conjugate base of HSO4- is __________.
a. | OH- |
b. | H2SO4 |
c. | SO42- |
d. | HSO4+ |
e. | H3SO4+ |
3.
The conjugate acid of HSO4- is __________.
a. | SO42- |
b. | H2SO4 |
c. | HSO4+ |
d. | H+ |
e. | HSO3+ |
4.
What is the conjugate base of OH-?
a. | O2 |
b. | O- |
c. | H2O |
d. | O2- |
e. | H3O+ |
5.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C in which
[H+] is 0.0025 M?
a. | 3.40 |
b. | 2.60 |
c. | -2.60 |
d. | -3.40 |
e. | 2.25 |
6.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C in which
[OH-] is 0.0025 M?
a. | +2.60 |
b. | -2.60 |
c. | +11.4 |
d. | -11.4 |
e. | -2.25 |
7.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 ´ 10-9 M hydronium ion?
a. | 8.400 |
b. | 5.600 |
c. | 9.000 |
d. | 3.980 |
e. | 7.000 |
8.
What is the pH of an aqueous solution at 25.0 °C that contains 3.98 ´ 10-9 M hydroxide ion?
a. | 8.40 |
b. | 5.60 |
c. | 9.00 |
d. | 3.98 |
e. | 7.00 |
9.
An aqueous solution contains 0.100 M NaOH at 25.0°C. The pH of the
solution is __________.
a. | 0.100 |
b. | 1.00 |
c. | 13.00 |
d. | 7.00 |
e. | -1.00 |
10.
HZ is a weak acid. An aqueous solution of HZ is prepared by dissolving 0.020 mol
of HZ in sufficient water to yield 1.0 L of solution. The pH of the solution was 4.93 at 25.0°C.
The Ka of HZ is __________.
a. | 1.2 ´ 10-5 |
b. | 6.9 ´ 10-9 |
c. | 1.4 ´ 10-10 |
d. | 9.9 ´ 10-2 |
e. | 2.8 ´ 10-12 |
11.
The pH of a 0.55 M aqueous solution of hypobromous acid, HBrO, at 25.0°C is
4.48. What is the value of Ka for HBrO?
a. | 2.0 ´ 10-9 |
b. | 1.1 ´ 10-9 |
c. | 6.0 ´ 10-5 |
d. | 3.3 ´ 10-5 |
e. | 3.0 ´ 104 |
12.
The Ka of hydrofluoric acid (HF) at 25.0°C is 6.8 ´ 10-4. What is the pH of a 0.35 M aqueous solution of
HF?
a. | 3.25 |
b. | 1.81 |
c. | 3.64 |
d. | 0.46 |
e. | 1.22 |
13.
Determine the pH of a 0.35 M aqueous solution of CH3NH2
(methylamine). The Kb of methylamine is 4.4 ´
10-4.
a. | 10.00 |
b. | 3.86 |
c. | 12.09 |
d. | 1.96 |
e. | 13.24 |
14.
The Ka for HCN is 4.9 ´
10-10. What is the value of Kb for CN-?
a. | 2.0 ´ 10-5 |
b. | 4.0 ´ 10-6 |
c. | 4.9 ´ 104 |
d. | 4.9 ´ 10-24 |
e. | 2.0 ´ 109 |
15.
The pH of a 0.15 M aqueous solution of NaZ (the sodium salt of HZ) is 10.7. What
is the Ka for HZ?
a. | 1.6 ´ 10-6 |
b. | 6.0 ´ 10-9 |
c. | 8.9 ´ 10-4 |
d. | 1.3 ´ 10-12 |
e. | 3.3 ´ 10-8 |
16.
According to the Arrhenius concept, an acid is a substance that
__________.
a. | is capable of donating one or more H+ |
b. | causes an increase in the concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions |
c. | can accept a pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond |
d. | reacts with the solvent to form the cation formed by autoionization of that solvent |
e. | tastes bitter |
17.
A Br nsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that
__________.
nsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that
__________.
a. | increases [H+] when placed in H2O |
b. | decreases [H+] when placed in H2O |
c. | increases [OH-] when placed in H2O |
d. | acts as a proton acceptor |
e. | acts as a proton donor |
18.
A Br nsted-Lowry acid is defined as a substance that
__________.
nsted-Lowry acid is defined as a substance that
__________.
a. | increases Ka when placed in H2O |
b. | decreases [H+] when placed in H2O |
c. | increases [OH-] when placed in H2O |
d. | acts as a proton acceptor |
e. | acts as a proton donor |
19.
A substance that is capable of acting as both an acid and as a base is
__________.
a. | autosomal |
b. | conjugated |
c. | amphoteric |
d. | saturated |
e. | miscible |
20.
The molar concentration of hydronium ion in pure water at 25°C is
__________.
a. | 0.00 |
b. | 1.0 ´ 10-7 |
c. | 1.0 ´ 10-14 |
d. | 1.00 |
e. | 7.00 |
21.
The magnitude of Kw indicates that __________.
a. | water autoionizes very slowly |
b. | water autoionizes very quickly |
c. | water autoionizes only to a very small extent |
d. | the autoionization of water is exothermic |
22.
In basic solution, __________.
a. | [H3O+] = [OH-] |
b. | [H3O+] > [OH-] |
c. | [H3O+] < [OH-] |
d. | [H3O+] = 0 M |
e. | [OH-] > 7.00 |
23.
Which solution below has the highest concentration of hydroxide ions?
a. | pH = 3.21 |
b. | pH = 12.6 |
c. | pH = 7.93 |
d. | pH = 9.82 |
e. | pH = 7.00 |
24.
Nitric acid is a strong acid. This means that __________.
a. | aqueous solutions of HNO3 contain equal concentrations of H+(aq) and OH-(aq) |
b. | HNO3 does not dissociate at all when it is dissolved in water |
c. | HNO3 dissociates completely to H+(aq) and NO3-(aq) when it dissolves in water |
d. | HNO3 produces a gaseous product when it is neutralized |
e. | HNO3 cannot be neutralized by a weak base |
25.
Of the following acids, __________ is not a strong acid.
a. | HNO2 |
b. | H2SO4 |
c. | HNO3 |
d. | HClO4 |
e. | HCl |
26.
Of the following, __________ is a weak acid.
a. | HF |
b. | HCl |
c. | HBr |
d. | HNO3 |
e. | HClO4 |
27.
Which one of the following is the weakest acid?
a. | HF (Ka = 6.8 ´ 10-4) |
b. | HClO (Ka = 3.0 ´ 10-8) |
c. | HNO2 (Ka = 4.5 ´ 10-4) |
d. | HCN (Ka = 4.9 ´ 10-10) |
e. | Acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 ´ 10-5) |
28.
Of the acids in the table below, __________ is the strongest acid.
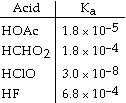

a. | HOAc |
b. | HCHO2 |
c. | HClO |
d. | HF |
e. | HOAc and HCHO2 |
29.
The Ka of hypochlorous acid (HClO) is 3.0 ´ 10-8 at 25.0°C . What is the %
ionization of hypochlorous acid in a 0.015 M aqueous solution of HClO at 25.0°C?
a. | 4.5 ´ 10-8 |
b. | 14 |
c. | 2.1 ´ 10-5 |
d. | 0.14 |
e. | 1.4 ´ 10-3 |
30.
Which one of the following is a BrÆnsted-Lowry
acid?
a. | (CH3)3NH+ |
b. | CH3COOH |
c. | HF |
d. | HNO2 |
e. | all of the above |
31.
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W) or strong acids
(S):
| benzoic acid | nitric acid | acetic acid |
a. | W W W |
b. | S S S |
c. | S W W |
d. | W S S |
e. | W S W |
32.
Classify the following compounds as weak acids (W) or strong acids
(S):
| nitrous acid | hydrochloric acid | hydrofluoric acid |
a. | W W W |
b. | S S S |
c. | S W W |
d. | W S S |
e. | W S W |
33.
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the strongest
base?
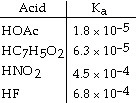

a. | OAc- |
b. | C7H5O2- |
c. | NO2- |
d. | F- |
e. | OAc- and C7H5O2- |
34.
Using the data in the table, which of the conjugate bases below is the weakest
base?
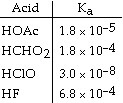

a. | OAc- |
b. | CHO2- |
c. | ClO- |
d. | F- |
e. | OAc- and CHO2- |
35.
Which of the following aqueous solutions has the lowest
[OH-]?
a. | a solution with a pH of 3.0 |
b. | a 1 ´ 10-4 M solution of HNO3 |
c. | a solution with a pOH of 12.0 |
d. | pure water |
e. | a 1 ´ 10-3 M solution of NH4Cl |
36.
Of the compounds below, a 0.1 M aqueous solution of __________ will have the
highest pH.
a. | KCN, Ka of HCN = 4.0 ´ 10-10 |
b. | NH4NO3, Kb of NH3 = 1.8 ´ 10-5 |
c. | NaOAc, Ka of HOAc = 1.8 ´ 10-5 |
d. | NaClO, Ka of HClO = 3.2 ´ 10-8 |
e. | NaHS, Kb of HS- = 1.8 ´ 10-7 |
37.
In the gas phase reaction below, NH3 is acting as a(n) __________
base but not as a(n) __________ base.
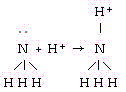
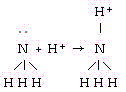
a. | Arrhenius, BrÆnsted-Lowry |
b. | BrÆnsted-Lowry, Lewis |
c. | Lewis, Arrhenius |
d. | Lewis, BrÆnsted-Lowry |
e. | Arrhenius, Lewis |