Mr. K AP Chemistry: Solution Properties Chpt 13 Brown et. al 11th edition
Quiz
- What is the mole fraction of ethanol, C2H5OH, in an aqueous solution that is 46 percent ethanol by mass? (The molar mass of C2H5OH is 46 g; the molar mass of H2O is 18 g.)
- 0.25
- 0.46
- 0.54
- 0.67
- 0.75
- The boiling points of the elements helium, neon, argon, krypton, and xenon increase in that order. Which of the following statements accounts for this increase?
- The London (dispersion) forces increase.
- The hydrogen bonding increases.
- The dipole-dipole forces increase.
- The chemical reactivity increases.
- The number of nearest neighbors increases.
- Which of the following substances is LEAST soluble in water?
- (NH4)2SO4
- KMnO4
- BaCO3
- Zn(NO3)2
- Na3PO4
- Which of the following describes the changes in forces of attraction that occur as H2O changes phase from a liquid to a vapor?
- H—O bonds break as H—H and O—O bonds form.
- Hydrogen bonds between H2O molecules are broken.
- Covalent bonds between H2O molecules are broken.
- Ionic bonds between H+ ions and OH– ions are broken.
- Covalent bonds between H+ ions and H2O molecules become more effective.
- Liquid naphthalene at 95˚C was cooled to 30˚C as represented in the cooling curve above. From which section of the curve can the melting point of naphthalene be determined?
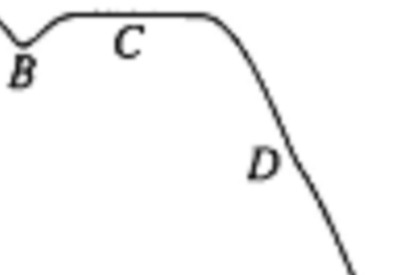
- A
- B
- C
- D
- E
- When a non-ideal gas occupies a volume that is less than the volume predicted by the ideal gas law, the explanation lies in the fact that the ideal gas law does not account for which of the following?
- Particle Volume
- Particle Mass
- Particle Velocity
- Intermolecular Forces
- Molecular Geometry
- Which of the following actions would be likely to change the boiling point of a pure liquid in an open container?
I. Placing the liquid in a smaller container.
II. Increasing the number of moles of liquid in the container.
III. Moving the container and liquid to a higher altitude.- I only
- II only
- III only
- II and III only
- I, II, and III
- Which of the following statements is always true at the Triple Point of a pure Substance?
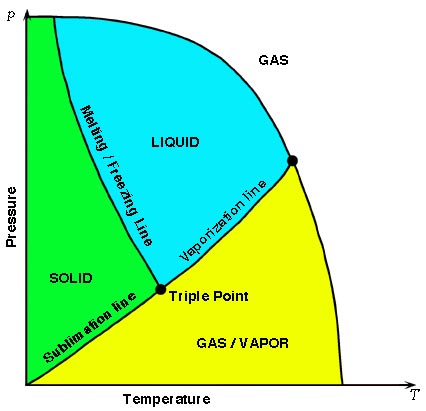
- The vapor pressure of the solid phase equals the pressure of the liquid phase.
- The temperature is always lower than the normal freezing temperature.
- The liquid phase always has the same density as the solid phase.
- The solid phase always melts if the pressure is increased at constant temperature.
- The liquid phase always vaporizes if the pressure is increased at constant temp.